Understanding Hardy vs. Tender Plants
When it comes to gardening, understanding the difference between hardy and tender plants is essential for growing a healthy landscape. Hardy plants are resilient and can thrive in colder climates, while tender varieties are delicate and require protection from frost.
This article explores the factors influencing plant hardiness and tenderness, showcasing the unique characteristics of both categories. You’ll also find practical care tips and guidance on selecting the ideal plants for your local climate, empowering you to make the best choices for your garden!
Immerse yourself in the nuances that can elevate your gardening endeavors!
Contents
Key Takeaways:

- Understanding the difference between hardy and tender plants is crucial for maintaining a successful garden.
- Climate and environmental conditions play a significant role in determining a plant’s hardiness and tenderness.
- Proper maintenance and protection are essential for caring for both hardy and tender plants, and selecting the right plants for your climate is key.
What is the Difference?
Grasping the distinctions between hardy and tender plants is crucial for any gardener. Hardy plants boast remarkable resilience, thriving even in colder temperatures.
On the other hand, tender plants need extra protection from harsh weather conditions. Understanding the characteristics of both can significantly enhance your gardening success.
Factors Affecting Hardiness and Tenderness
Several factors influence the hardiness and tenderness of your plants, including climate and soil quality. Knowing your local USDA Hardiness Zone a system that helps you know which plants will thrive in your area is essential.
This knowledge guides you in selecting the right seeds and seedlings, ensuring your garden flourishes beautifully. It also informs you about the minimum temperatures your plants can endure.
Climate and Environmental Conditions
Climate and environmental conditions are crucial for plant growth. Variations in temperature can lead to frost damage or hinder the germination of young seedlings.
Don t miss out on the chance to protect your tender plants from unexpected frost! For example, sudden drops in temperature can harm tender species, like tomatoes and peppers.
These plants might suffer from leaf burn or reduced yield due to unexpected frost. In contrast, hardy plants like kale and Brussels sprouts often thrive in cooler conditions.
In areas where early spring frosts are common, your timing is crucial. Delaying your planting could mean the difference between a bountiful harvest and a disappointing crop.
Hardy Plants: Characteristics and Examples

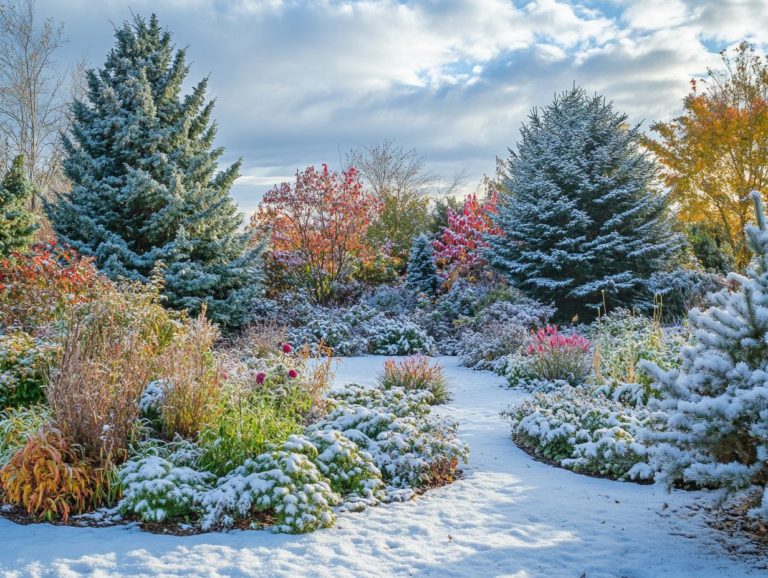
Hardy plants stand out for their remarkable resilience to cold temperatures and harsh weather conditions. They can flourish even in the most demanding climates and throughout the winter months.
These botanical marvels possess adaptations, such as enhanced frost tolerance and deep root systems. This makes them ideal choices for gardens situated in regions with significant climate challenges.
Adaptations for Cold and Harsh Conditions
Hardy plants have unique adaptations that help them thrive in extreme weather. They can withstand frost and long cold spells with their remarkable traits.
Some plants have specialized leaf structures that minimize water loss and protect against ice damage. For example, conifers like spruce and pine have needle-like leaves with a waxy coating. This helps them keep moisture and survive freezing temperatures.
Certain perennials stand out by storing energy in their root systems. This allows them to bounce back quickly when warm weather returns. These special traits boost their resilience, allowing them to thrive where other plants might struggle.
Tender Plants: Characteristics and Examples
Tender plants need careful attention due to their sensitivity to cold and frost. To ensure their growth and survival in harsher climates, implementing protective measures is essential.
Start these delicate specimens indoors or in a greenhouse. When it’s time to transplant them outdoors, consider using cloches or covers to protect them from sudden temperature drops. This enhances their chances of thriving in the open air.
Sensitivity to Cold and Frost
Sensitivity to cold and frost defines tender plants, which require specific temperature ranges to flourish. They can suffer irreversible damage if exposed to freezing conditions. This vulnerability makes it essential to monitor local temperatures and adopt protective strategies during colder months.
Understanding the specific temperature thresholds for these delicate species is crucial. For instance, the common geranium begins to show stress at temperatures below 50 F, while the beloved hibiscus might not survive even a light frost. Remain vigilant as temperatures dip and consider methods like covering your plants with frost cloth or moving potted specimens indoors to shield them from the elements.
Familiarity with each plant s ideal growing conditions can make a significant difference. By taking proactive measures, you can help your tender plants withstand the chill and emerge healthy as spring unfolds.
Caring for Hardy and Tender Plants

Caring for hardy and tender plants can be a rewarding adventure! It requires a nuanced approach that promotes their optimal growth and survival. Focus on practices such as proper watering, fertilizing, and the essential hardening-off process for young seedlings.
With hardy plants, appreciating their resilience means you can adopt a more hands-off care routine. In contrast, tender plants demand a little extra attention and protective measures to flourish successfully.
Tips for Proper Maintenance and Protection
Proper maintenance and protection are essential for ensuring the health and longevity of both hardy and tender plants. By employing techniques such as cloches, cold frames, and mulch, you can create an ideal environment for growth.
For instance, cloches can be particularly beneficial in early spring, acting as mini-greenhouses that protect delicate seedlings from unexpected frost. Cold frames provide a more permanent solution, allowing you to gradually harden off young plants while extending the growing season.
A layer of mulch does double duty by conserving moisture during dry spells and suppressing weed growth, which competes for essential nutrients.
By implementing these methods, you can significantly boost plant health and ensure vibrant blooms and fruitful harvests throughout the growing year. Start implementing these tips today to ensure your plants flourish all year round!
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Garden
Selecting the right plants for your garden is essential. It is influenced by your local climate, plant survival zones, and the aesthetic vision you wish to achieve.
Understanding the differences between plant species empowers you to choose those that will thrive in your environment. This knowledge is crucial for a flourishing garden.
Determining Hardiness and Tenderness for Your Climate
To pick the right plants for your climate, you need to understand what your plants require. Knowing your area’s average temperatures, frost dates, and soil conditions is vital for making informed decisions about which plants to cultivate.
Start by assessing a map that shows which plants can survive in your area s climate; this will help you pinpoint your specific zone and identify which plants are most likely to thrive. Pay attention to microclimates small areas that have slightly different weather conditions than the surrounding region. Elements such as wind exposure, sunlight patterns, and moisture levels significantly influence plant selection.
Next, research native species that are already well-adapted to your local conditions. This can provide a solid foundation for creating a resilient garden. Understanding these climatic elements will guide you in choosing plants that not only survive but also flourish beautifully within your landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between hardy and tender plants?
Hardy plants can survive in cold temperatures and harsh conditions, while tender plants are more delicate and need warmer temperatures and protection from extreme weather.
How can I tell if a plant is hardy or tender?
A general rule of thumb is that plants with thicker, woody stems and smaller leaves are more likely to be hardy. In contrast, plants with thinner stems and larger leaves are more likely to be tender. However, it’s always best to research the specific plant’s survival zone before planting.
Which plants are considered hardy?
Common examples of hardy plants include conifers, like pine and spruce trees, as well as perennials such as daylilies and peonies.
Do hardy plants require any special care?
Hardy plants are more resilient and typically can survive on their own without much care. However, it’s still important to provide them with adequate water and nutrients to promote healthy growth.
What types of plants are considered tender?
Tender plants are usually tropical or subtropical, such as orchids, palms, and some annual flowers like impatiens and begonias.
How should I care for tender plants?
Tender plants require more attention, especially during colder months. They should be brought indoors or protected from frost and extreme temperatures. Regular watering and fertilizing are essential for them to thrive.
Have questions about your gardening experiences? Feel free to leave a comment below!